In an increasingly interconnected business environment, a single vulnerability can unravel an entire organization. As cyber threats evolve with alarming speed, relying on outdated security measures is like defending a modern fortress with a wooden fence. The key to resilient defense lies in a proactive, multi-layered strategy that anticipates and neutralizes risks before they escalate into costly breaches. This guide moves beyond generic advice, offering a comprehensive roundup of the most critical network security best practices your business must implement.
Each practice detailed here is a vital component of a modern security architecture, designed to protect your sensitive data, maintain operational integrity, and secure your long-term viability. From implementing a Zero Trust model to refining your incident response plan, these strategies are essential for any organization, especially those in regulated industries like healthcare or finance where compliance is non-negotiable. Building a robust defense requires a clear blueprint. For those architecting their security from the ground up, understanding Comprehensive Network Security Design Principles provides a foundational framework for integrating these controls effectively.
We will explore actionable strategies that form the bedrock of a robust and adaptive security posture. This listicle provides the implementation details, real-world examples, and clear guidance necessary to transform your network from a potential liability into a fortified asset. Let's examine the essential practices for strengthening your digital defenses.
1. Zero Trust Architecture
The traditional "castle-and-moat" approach to network security, which trusts anyone and anything inside the firewall, is no longer sufficient. A Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) fundamentally shifts this paradigm, operating on the principle of "never trust, always verify." This modern framework eliminates implicit trust by continuously validating every stage of digital interaction, effectively treating all access requests as if they originate from an open, untrusted network.

Instead of a one-time authentication at the perimeter, Zero Trust demands strict identity and device verification for every user and system attempting to access resources on the network. This granular, per-request access control model significantly reduces the attack surface and prevents lateral movement by malicious actors who may have breached the perimeter. It is a vital strategy for protecting sensitive data, especially for businesses with remote employees, cloud environments, and complex supply chains.
How to Implement a Zero Trust Framework
Adopting a Zero Trust model is a journey, not an overnight switch. It requires a strategic, phased approach focused on building layers of verification and control. Here are actionable steps to begin:
- Identify Critical Assets: Start by mapping your most sensitive data, applications, and services. You cannot protect what you don't know you have. This initial step informs where to apply the strictest controls first.
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA is a cornerstone of Zero Trust. Deploying it across all user accounts, especially for privileged access, creates an immediate and powerful security uplift.
- Utilize Microsegmentation: Break your network into small, isolated zones. This practice, known as microsegmentation, contains potential breaches by preventing unauthorized lateral movement between different parts of your network. For example, the finance department's servers should be inaccessible from the marketing department's network segment without explicit, verified permission.
- Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM): A robust IAM solution ensures that only the right individuals have access to the right resources, for the right reasons. This involves enforcing the principle of least privilege, granting users the minimum access necessary to perform their jobs.
By adopting these network security best practices, organizations can build a resilient defense that adapts to modern threats, protecting critical assets regardless of where they are located.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Relying solely on passwords for network security is a dangerous gamble, as credentials can be easily stolen, guessed, or cracked. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) provides a critical layer of defense by requiring users to present two or more distinct verification factors to gain access. This method creates a layered barrier, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to access your network, even if they have a compromised password.

MFA works by combining something the user knows (a password), something they have (a smartphone app like Google Authenticator or a hardware token like a YubiKey), and/or something they are (a fingerprint or facial scan). By demanding this additional proof of identity, MFA ensures that a stolen password alone is not enough to breach your defenses. For regulated industries like healthcare and finance, implementing MFA is not just a best practice; it is often a core compliance requirement for protecting sensitive data.
How to Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
A successful MFA rollout enhances security without creating unnecessary friction for users. A phased and strategic approach is key to adoption and effectiveness. Here are actionable steps for implementation:
- Prioritize High-Risk Accounts: Begin by deploying MFA for administrators, executives, and other users with privileged access to critical systems and sensitive data. This immediately protects your most valuable assets.
- Choose the Right Authentication Factors: While SMS-based codes are better than nothing, they are vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks. Prioritize more secure methods like authenticator apps (e.g., Microsoft Authenticator) or physical hardware keys for the highest level of protection.
- Consider Adaptive MFA: Implement an adaptive or risk-based MFA solution. This technology can dynamically adjust authentication requirements based on context, such as user location, device, or time of day. For example, it might not prompt for MFA from a trusted device on the corporate network but will require it from an unrecognized device in a different country.
- Educate and Prepare Your Team: Before a full rollout, communicate the "why" behind MFA to your users. Provide clear instructions, training materials, and support channels to ensure a smooth transition and reduce help desk requests. Ensure users set up backup options and store recovery codes securely.
3. Regular Security Patches and Updates
Neglecting software updates is like leaving a side door to your network wide open. A robust patch management strategy involves the systematic process of identifying, acquiring, testing, and installing critical code changes (patches) to your operating systems, applications, and firmware. This is a fundamental network security best practice because cybercriminals actively develop exploits for known vulnerabilities, making unpatched systems prime targets for attack.
The infamous 2017 Equifax breach, which exposed the personal data of 147 million people, was a direct result of failing to patch a known vulnerability in the Apache Struts web framework. Similarly, the WannaCry ransomware attack exploited an unpatched Windows vulnerability, crippling organizations worldwide. These incidents highlight that consistent patching is not just routine maintenance; it is an active defense against evolving threats.
How to Implement a Patch Management Program
A successful patch management program moves beyond reactive fixes to become a proactive, structured process. It ensures vulnerabilities are addressed before they can be exploited. Here are actionable steps to build an effective program:
- Create a Comprehensive Asset Inventory: You cannot protect what you do not know you have. Maintain a detailed inventory of all hardware and software assets on your network to ensure every component is included in your patching schedule.
- Automate the Patching Process: Manually updating every system is inefficient and prone to error. Utilize automated patch management tools like Microsoft WSUS or cloud-based solutions like AWS Systems Manager to streamline the deployment of updates across your network.
- Test Patches Before Deployment: Always test patches in a controlled, non-production environment first. This crucial step prevents a faulty update from causing operational disruptions or system instability when deployed to your live network.
- Prioritize and Schedule Effectively: Not all patches are equal. Prioritize the immediate deployment of critical security patches that address severe vulnerabilities. Establish a regular, predictable schedule, such as monthly, for routine updates to ensure consistency and minimize disruption.
4. Network Segmentation and Firewalls
Just as a ship uses bulkheads to contain flooding, network segmentation divides a larger network into smaller, isolated subnetworks. This practice, when combined with strategically placed firewalls, creates a powerful security architecture that contains threats and limits an attacker's ability to move laterally across your digital environment. Firewalls act as the gatekeepers, inspecting traffic between these segments and enforcing strict access rules.

This approach is one of the most effective network security best practices for minimizing the blast radius of a potential breach. If one segment is compromised, such as a guest Wi-Fi network, the firewalls prevent the threat from spreading to critical zones like the one containing sensitive financial data. This layered defense is crucial for compliance with regulations like PCI DSS, which mandates the isolation of cardholder data environments, and for protecting critical infrastructure in sectors like healthcare.
How to Implement Network Segmentation
Effective segmentation requires careful planning and robust technology. It's a foundational security measure that significantly enhances an organization's defensive posture. Here are actionable steps to get started:
- Create Security Zones: Begin by mapping your network and classifying assets based on their function and sensitivity. Create logical zones, such as a separate segment for public-facing servers, another for internal user workstations, and a highly restricted zone for critical data servers.
- Deploy Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): Use NGFWs with deep packet inspection capabilities at the boundaries of each segment. These devices go beyond simple port and protocol filtering, allowing you to enforce policies based on application, user identity, and content.
- Implement Least Privilege Access: Configure firewall rules to enforce the principle of least privilege. This means traffic between segments should be denied by default, and only explicitly allowed connections necessary for business operations should be permitted.
- Monitor Inter-Segment Traffic: Continuously monitor the traffic flowing between your network segments for unusual patterns or policy violations. Anomalous activity could be an early indicator of a security incident, and having managed cybersecurity services can provide the 24/7 monitoring needed to detect these threats.
5. Employee Security Awareness Training
While sophisticated firewalls and advanced threat detection systems are essential, an organization's security is often only as strong as its least aware employee. Employee security awareness training is a critical program designed to educate staff about cybersecurity risks, how to recognize threats, and the importance of following security protocols. Since human error is a factor in a vast majority of security breaches, empowering employees to act as a human firewall is one of the most effective network security best practices.
This ongoing educational process transforms employees from potential liabilities into a proactive line of defense. It equips them to identify phishing attempts, understand the need for strong passwords, handle sensitive data correctly, and confidently report suspicious activity. For organizations in regulated industries like healthcare or finance, effective training, such as HIPAA compliance programs, is not just a best practice but a legal necessity.
How to Implement Security Awareness Training
A successful training program is continuous and engaging, not a one-time event. It should be woven into the company culture to build a security-conscious mindset. Here are actionable steps to build an effective program:
- Run Regular Phishing Simulations: The most effective way to teach is by doing. Use platforms like KnowBe4 to send simulated phishing emails to employees. These controlled tests help staff recognize real-world threats in a safe environment and provide measurable data on their progress.
- Make Training Engaging and Relevant: Move beyond dry presentations. Use interactive modules, videos, quizzes, and real-world scenarios of recent threats to keep employees engaged. Tailor content to specific roles; for instance, the finance team needs training on business email compromise, while IT needs advanced threat training. To further enhance your human firewall, consider exploring effective employee security awareness training strategies.
- Establish a Positive Security Culture: Encourage reporting and reward vigilance. Create a clear, non-punitive process for employees to report suspicious emails or potential incidents. Recognizing and rewarding employees who identify threats fosters a proactive culture where everyone feels responsible for security.
- Integrate Training into the Employee Lifecycle: Security awareness should begin on day one. Incorporate foundational training into your onboarding process for all new hires and provide regular, mandatory refresher courses at least quarterly to keep security top-of-mind.
6. Data Encryption (In Transit and At Rest)
In today's data-driven world, information is a company's most valuable asset. Data encryption is the practice of converting this information into a coded format, rendering it unreadable to anyone without the specific decryption key. This fundamental security control is non-negotiable for protecting sensitive information, ensuring that even if data is intercepted during transit across a network or stolen while at rest on a server or device, it remains completely useless to unauthorized parties.
Encrypting data in transit protects it as it travels between systems, such as when a user accesses a website (via HTTPS) or sends a secure message (using end-to-end encryption like Signal). Encrypting data at rest secures it when stored, which includes files on laptops (using BitLocker or FileVault), databases holding customer information, or data archived in the cloud. Implementing both forms is a cornerstone of a robust security posture and a key requirement for compliance standards like HIPAA and GDPR.
How to Implement Comprehensive Data Encryption
Effective encryption involves more than just flipping a switch; it requires a deliberate strategy covering all stages of the data lifecycle. A layered approach ensures there are no gaps in your data protection strategy. Here are actionable steps to implement encryption:
- Standardize Strong Encryption Protocols: Mandate the use of industry-standard algorithms like AES-256 for data at rest and TLS 1.3 for data in transit. It is equally important to explicitly disable outdated and vulnerable protocols such as SSL and early versions of TLS.
- Enforce Full-Disk Encryption (FDE): Ensure that all company endpoints, including laptops, mobile devices, and servers, have FDE enabled. Tools like Microsoft's BitLocker and Apple's FileVault make this a straightforward process that protects data if a device is lost or stolen.
- Secure All Web and Network Traffic: Implement HTTPS across all websites and internal web applications using TLS certificates. For remote access and site-to-site connections, use a properly configured VPN that employs strong encryption protocols like IPsec to create a secure tunnel for data.
- Manage Encryption Keys Securely: The security of your encrypted data is entirely dependent on the security of your decryption keys. Use a centralized key management system (KMS) or a hardware security module (HSM) for high-security environments to protect, rotate, and manage keys throughout their lifecycle.
By making data encryption a core component of your security framework, you create a powerful last line of defense. As one of the most critical network security best practices, it demonstrates a commitment to protecting sensitive information, which is fundamental for any growing business. To delve deeper into how these measures support business growth, learn more about the importance of cybersecurity on defenditservices.com.
7. Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
A proactive approach to security involves more than just building strong defenses; it requires regularly testing those defenses for weaknesses. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are systematic evaluations of your network, policies, and procedures. This practice helps identify exploitable security flaws before malicious actors can discover them, ensuring your security posture remains robust against evolving threats.
While often used together, audits and assessments serve different functions. Vulnerability assessments use automated tools like Nessus or Qualys to scan for known flaws, whereas security audits are a more comprehensive review of whether security controls are correctly implemented and compliant with standards like PCI DSS or HIPAA. Combining these practices provides a holistic view of your security landscape, highlighting both technical vulnerabilities and procedural gaps.
How to Implement Audits and Assessments
Integrating regular testing into your security program is a critical network security best practice that transforms your defense from a static wall into a dynamic, adaptable shield. Here are actionable steps to get started:
- Establish a Testing Cadence: Create a consistent schedule for your security evaluations. Conduct automated vulnerability scans at least monthly, and schedule more intensive penetration tests annually or after any significant changes to your network infrastructure.
- Combine Automated and Manual Testing: Use automated scanners for broad, continuous coverage to catch common vulnerabilities. Complement this with manual penetration testing performed by skilled security professionals who can uncover complex business logic flaws and other issues that automated tools might miss.
- Prioritize and Remediate Findings: Not all vulnerabilities carry the same risk. Prioritize remediation efforts based on the potential impact and exploitability of each finding. Develop a clear action plan with assigned responsibilities and deadlines to ensure all critical issues are addressed promptly.
- Engage Third-Party Experts: For an unbiased and thorough evaluation, engage a third-party security firm. External auditors bring a fresh perspective and specialized expertise, which is often a requirement for compliance certifications like SOC 2 or ISO 27001.
8. Strong Password Policies and Password Management
Passwords remain the primary line of defense for accessing critical systems and data, yet they are often the weakest link. A strong password policy establishes clear rules for creating, managing, and protecting credentials across an organization. This goes beyond simple complexity requirements to address password lifecycle management, preventing reuse, and prohibiting sharing. When combined with a robust password management solution, it dramatically mitigates the risk of credential-stuffing, brute-force, and phishing attacks.
Effective password management is a foundational element of any network security best practices framework. It moves users away from weak, reused, or easily guessable passwords toward long, unique passphrases that are securely stored and easily accessible. Enterprise password managers, such as 1Password, Bitwarden, or LastPass, help enforce these policies by generating complex passwords, storing them in an encrypted vault, and simplifying secure access for employees. This approach reduces password fatigue and the unsafe practice of writing credentials down or saving them in unsecured files.
The following infographic outlines a simple yet powerful three-step process for employees to create and manage secure credentials, reinforcing the core principles of a modern password policy.
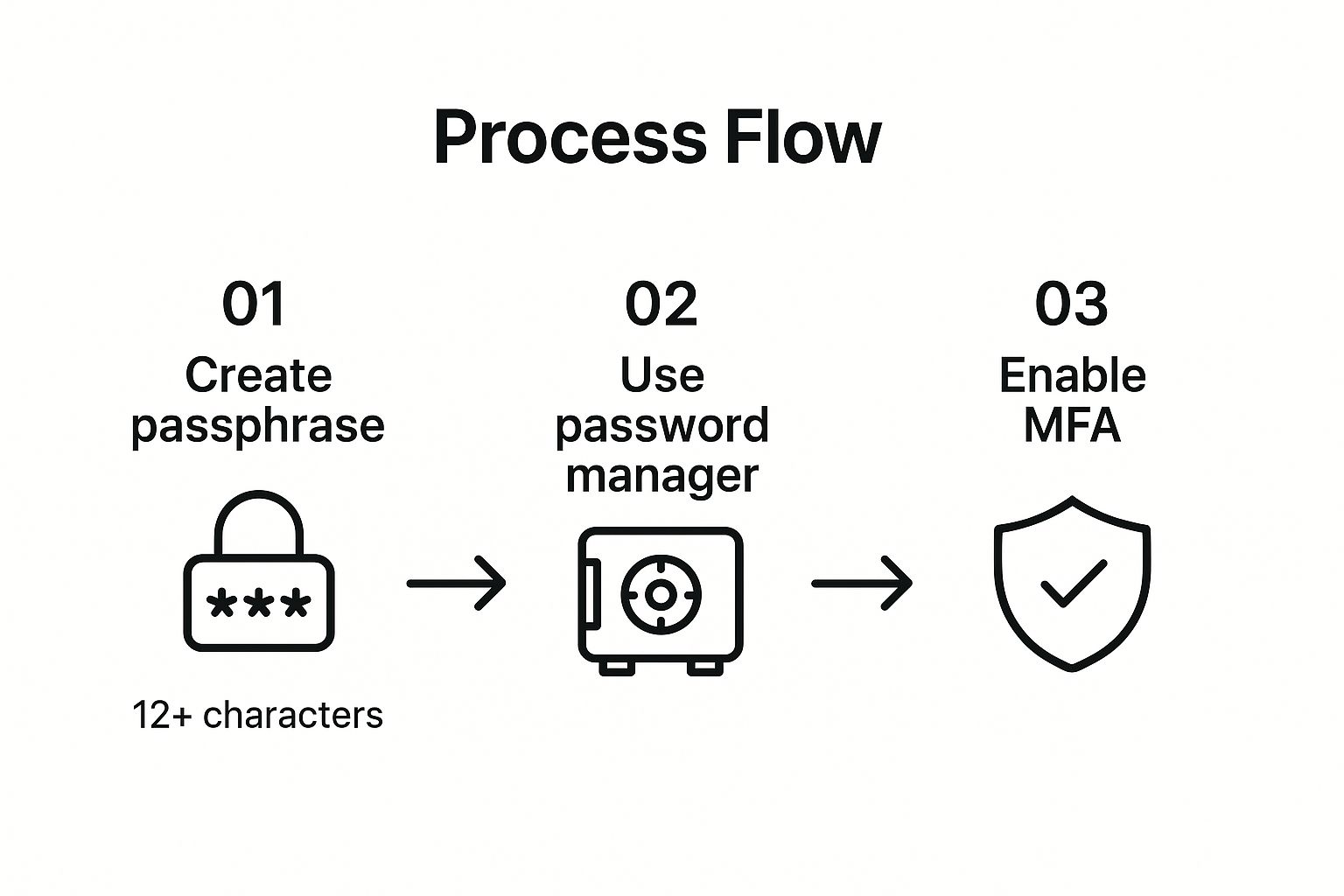
This process flow highlights that a strong, unique passphrase, secured within a password manager and backed by multi-factor authentication, creates a formidable layered defense for each account.
How to Implement Strong Password Policies
Implementing an effective policy requires a combination of technical controls and user education. It's not just about setting rules but enabling employees to follow them securely and efficiently.
- Enforce Length and Uniqueness: Following modern NIST guidelines, prioritize password length over forced complexity. Mandate a minimum of 12-16 characters and encourage the use of passphrases. Crucially, use tools to prevent password reuse across different systems.
- Deploy an Enterprise Password Manager: Provide all employees with a sanctioned, business-grade password manager. This centralizes credential management, allows for secure sharing within teams, and provides administrators with oversight and auditing capabilities.
- Integrate with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Passwords alone are not enough. MFA adds a critical verification layer, ensuring that even if a password is compromised, the attacker cannot gain access without the second factor. This is one of the most vital network security best practices to implement.
- Audit Against Known Breaches: Regularly check employee passwords against databases of known compromised credentials, like Have I Been Pwned. This proactive step helps identify and remediate vulnerable accounts before they can be exploited.
9. Incident Response Plan and Security Monitoring
A proactive defense is essential, but no security posture is impenetrable. An Incident Response Plan (IRP) is a documented, structured approach for how your organization will detect, respond to, and recover from a cybersecurity incident. This plan is not a standalone document; it is a live strategy powered by continuous security monitoring tools like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) and IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems).
The combination of a clear plan and active monitoring ensures that when a breach occurs, the response is swift, coordinated, and effective, rather than chaotic. This practice is crucial for minimizing the financial and reputational damage of an attack. The infamous 2017 Equifax breach, which was heavily criticized for its delayed response, serves as a stark reminder of what happens without a prepared, well-rehearsed plan. In contrast, Maersk's recovery from the NotPetya attack demonstrated resilience by rebuilding 4,000 servers in just 10 days, guided by a robust response strategy.
How to Implement Incident Response and Monitoring
Building a resilient incident response capability involves creating a clear framework and equipping your team with the right tools and training. Here are the foundational steps:
- Develop a Formal IRP: Create a written incident response plan, ideally following a recognized framework like the NIST Computer Security Incident Handling Guide. This document should clearly define what constitutes an incident, roles and responsibilities, and communication protocols.
- Establish a Dedicated Response Team: Form a Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT) with clearly defined roles, from technical analysts to legal and communications personnel. Ensure everyone understands their duties and has a clear escalation path.
- Deploy Centralized Monitoring Tools: Implement a SIEM system like Splunk to aggregate and correlate logs from across your network. This provides a single pane of glass for threat detection and simplifies forensic analysis during an investigation.
- Conduct Regular Drills: A plan is only effective if it's tested. Run quarterly tabletop exercises and simulations to test your playbooks for common scenarios like ransomware or data exfiltration. These drills identify weaknesses and ensure your team is prepared to act decisively under pressure.
By integrating these network security best practices, organizations can dramatically reduce recovery time and costs following a security event. For businesses seeking expert guidance on building these capabilities, trusted cybersecurity and IT solutions can provide the necessary framework and support.
10. Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
Even the most robust network defenses can be breached. When a cyberattack, hardware failure, or natural disaster strikes, a comprehensive Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) plan is the final, critical line of defense. This strategy involves more than just copying data; it's a documented, tested process for restoring systems and resuming operations with minimal downtime and data loss. Without a BDR plan, an organization risks catastrophic financial and reputational damage from which it may never recover.
The Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in 2021 serves as a stark reminder. Uncertainty about the viability of their backups reportedly influenced their decision to pay a multi-million dollar ransom. A well-executed BDR strategy ensures business continuity by making recovery a predictable, manageable process rather than a desperate gamble. This is a foundational component of any mature network security best practices framework.
How to Implement a Backup and Disaster Recovery Plan
A successful BDR strategy is built on redundancy, security, and regular testing. It ensures that even if primary systems and data are compromised, a clean, restorable copy is always available. Here are actionable steps to build a resilient BDR plan:
- Follow the 3-2-1-1 Rule: This is the gold standard for data protection. Maintain at least three copies of your data, on two different types of media, with one copy stored offsite, and one copy that is air-gapped or immutable. This layered approach protects against everything from a single drive failure to a ransomware attack that encrypts network-connected backups.
- Make Backups Immutable and Air-Gapped: Modern ransomware specifically targets and encrypts backup files. Immutable backups cannot be altered or deleted for a set period, while air-gapped backups are physically disconnected from the network. Both are essential safeguards against these advanced threats.
- Test Your Restores Regularly: Backups are useless if they cannot be restored. Schedule and perform regular tests of your recovery procedures, from individual file restores to full server virtualization. This validates your data integrity and ensures your IT team can execute the plan efficiently under pressure.
- Define RTO and RPO: Establish clear Recovery Time Objectives (RTO), which dictate how quickly you must be operational after a disaster, and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO), which define the maximum amount of data you can afford to lose. These metrics will guide your backup frequency and technology choices.
Network Security Best Practices Comparison
| Security Control/Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Trust Architecture | High – complex, 6-24 months, organizational change needed | Significant infrastructure and management | Granular access control, reduced attack surface | Enterprises with sophisticated infrastructure, remote work environments | Strong protection against insider threats, supports compliance |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Low to Medium – relatively easy to deploy | Moderate (tokens, apps management) | Drastically reduces account compromise risk | Web services, enterprise accounts, VPN access | Blocks 99.9% of automated attacks, cost-effective security boost |
| Regular Security Patches and Updates | Medium – requires ongoing scheduling and testing | Moderate IT staff and automated tools | Closes vulnerabilities, improves stability | All organizations maintaining software lifecycle | Prevents common exploit routes, maintains compliance |
| Network Segmentation and Firewalls | Medium to High – network redesign and ruleset management | Skilled network personnel and firewall hardware/software | Limits lateral threat movement, contains breaches | Networks requiring zone-based security, regulated industries | Reduces attack surface, improves network performance |
| Employee Security Awareness Training | Medium – requires ongoing commitment | Low to Moderate (training platforms and time) | Reduces human error, improves incident reporting | All organizations facing insider risk | Creates security culture, cost-effective, reduces phishing success |
| Data Encryption (In Transit and At Rest) | Medium – technical setup, key management | Moderate to High (encryption hardware/software) | Data confidentiality maintained even in breaches | Organizations handling sensitive data, compliance-driven industries | Protects data integrity and privacy, mandatory for many regulations |
| Regular Security Audits & Vulnerability Assessments | Medium to High – specialized skills and time investment | Moderate to High (tools, external experts) | Identifies vulnerabilities, validates controls | Organizations requiring compliance and proactive risk management | Provides actionable remediation, demonstrates due diligence |
| Strong Password Policies & Management | Low to Medium – policy enforcement and tools | Low to Moderate (password managers, training) | Reduces credential-based attacks | All organizations with user accounts | Simplifies password use, enhances security posture |
| Incident Response Plan & Security Monitoring | High – planning, 24/7 monitoring, skilled staff | High (SIEM, analysts, tools) | Faster detection and containment of incidents | Organizations needing rapid breach response | Minimizes impact and recovery time, ensures coordination |
| Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning | Medium to High – backup systems and procedures | Moderate to High (storage, testing, management) | Business continuity, data recovery capability | All organizations needing resilience against data loss | Enables recovery from ransomware and failures, regulatory compliance |
From Theory to Practice: Securing Your Network with Expert Guidance
Navigating the complex landscape of digital threats requires more than just awareness; it demands a proactive, layered, and continuously evolving defense. Throughout this guide, we've explored ten foundational network security best practices, moving from high-level architectural shifts like Zero Trust to the granular, everyday habits of strong password hygiene and employee training. Each practice represents a critical pillar in a comprehensive security framework, designed not as an isolated fix but as an interconnected part of a resilient digital ecosystem.
The journey from understanding these concepts to implementing them effectively can be daunting. You now know that simply installing a firewall is insufficient. True security lies in meticulous network segmentation, ensuring that a breach in one area is contained and cannot spread laterally across your entire infrastructure. Similarly, acknowledging the importance of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is the first step; the next is deploying it universally across all critical systems, from email to VPN access, creating a formidable barrier against credential theft.
The Interconnected Web of Modern Defense
It's crucial to recognize how these practices reinforce one another. A robust backup and disaster recovery plan becomes even more powerful when combined with strong data encryption, ensuring that even if data is stolen, it remains unreadable and useless to attackers. Your incident response plan, a theoretical document, is only as effective as the 24/7 security monitoring that feeds it real-time alerts.
Consider these key takeaways as the core of your strategy:
- Proactive vs. Reactive: Don't wait for a breach. Regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and consistent patching are proactive measures that close security gaps before they can be exploited.
- The Human Element: Technology alone cannot secure your network. Continuous employee security awareness training transforms your team from a potential vulnerability into your first line of defense, capable of identifying phishing attempts and social engineering tactics.
- Assume Breach Mentality: The Zero Trust model ("never trust, always verify") is the guiding principle of modern security. It forces you to build defenses from the inside out, protecting your most valuable assets with micro-segmentation and strict access controls.
From Knowledge to Action: Your Next Steps
Implementing these network security best practices is not a one-time project but a perpetual commitment. For small and midsize businesses, especially those in regulated industries like healthcare or finance, maintaining this level of vigilance can strain internal resources. The expertise required to conduct thorough risk assessments, manage a 24/7 Security Operations Center (SOC), and ensure compliance with standards like HIPAA is a full-time job.
This is where a strategic partnership becomes a powerful asset. By offloading the complex, time-consuming tasks of network management and cybersecurity to a dedicated team, you free up your internal staff to focus on core business objectives. You gain access to enterprise-grade tools, specialized expertise, and the peace of mind that comes from knowing your digital fortress is being monitored around the clock by seasoned professionals. Ultimately, investing in expert guidance is not just an IT expense; it's a strategic investment in business continuity, reputation protection, and long-term growth. Your network is the backbone of your operations; securing it is paramount.
Ready to transform these network security best practices from a checklist into a fully managed, robust defense? Partner with Defend IT Services, a veteran-owned team in San Antonio, to build and maintain your digital fortress with 24/7 monitoring and expert support. Contact Defend IT Services today to schedule a consultation and secure your business for the future.

