All the best security software in the world can’t stop a ransomware attack if an employee clicks a malicious link. The simple, uncomfortable truth is that cybercriminals rarely have to break down your digital door; they just trick someone into opening it for them.
Your technology is a critical piece of the puzzle, but without well-trained, vigilant employees, you're leaving a massive gap in your defenses. This is where building a "human firewall" becomes one of the most effective strategies you can adopt.
Building Your Human Firewall Against Ransomware

A human firewall isn’t about a single, mind-numbing annual seminar that everyone forgets by lunchtime. It's about cultivating a deep-rooted culture of security awareness where every single person on your team understands their role in protecting the business.
Think of it as transforming your employees from potential targets into your first and best line of defense. It’s a continuous effort, not a one-and-done task.
Move Beyond One-Off Training
If you want security habits to stick, they need to be woven into the fabric of your daily operations. A successful security awareness program is a marathon, not a sprint. The goal is to make secure practices second nature.
Here’s how you can make your training truly effective:
- Make It Engaging: Ditch the dry, text-heavy presentations. Use short videos, interactive quizzes, and discussions about real-world security breaches instead.
- Keep It Frequent: A five-minute training video once a month or a weekly security tip in your company newsletter is far more impactful than a three-hour session once a year.
- Ensure It's Relevant: The threats facing your accounting team are different from those targeting your sales staff. Tailor the training with examples they’ll actually encounter in their day-to-day work.
For any growing business, getting the team to understand the why behind these practices is crucial. We dig deeper into this concept in our article on https://defenditservices.com/the-importance-of-cybersecurity-for-growing-businesses/, which lays the foundation for building a strong security culture.
Run Phishing Simulations That Actually Teach
Phishing tests are an incredibly powerful tool, but only if you use them to educate, not to shame. The objective isn't to catch people out; it's to give them a safe space to make a mistake and, more importantly, to learn from it.
A poorly run simulation just creates resentment. A well-designed one, however, builds resilience. Instead of a generic "You clicked!" message, provide immediate, constructive feedback. Walk the user through the exact red flags they missed—was it the slightly-off sender address, the urgent and demanding language, or the suspicious link? This turns a slip-up into a powerful, lasting lesson.
A key shift in mindset is viewing a "click" not as a failure, but as a teachable moment. When an employee reports a simulation, celebrate it. This reinforces positive behavior and encourages vigilance across the entire organization.
Deconstruct the Psychology of Attacks
Cybercriminals are masters of manipulation. They prey on basic human emotions like trust, urgency, and fear to bypass our rational thinking. Your team needs to understand these psychological tricks to become immune to them.
Break down real-world attack examples with your team. Show them how these tactics work in practice:
- The CEO Fraud: An email that looks like it’s from an executive demanding an urgent wire transfer to a new vendor.
- The Fake Invoice: A message with an attachment claiming to be an overdue bill, designed to create panic and a knee-jerk click.
- The Credential Harvester: A link to a fake Microsoft 365 or Google login page that looks identical to the real thing, designed to steal passwords.
By understanding the why behind an attack, your team gets much better at spotting the how. The data makes this urgency crystal clear. In 2025, phishing was the trigger for 18% of all ransomware attacks globally, a shocking jump from 11% the year before. This sharp rise shows just how critical it is to harden your first line of defense with effective security awareness training.
The same report found that 96% of ransomware attacks also go after backup systems, proving that you need a multi-layered defense that combines a savvy team with solid technical safeguards.
Hardening Your Technical Defenses and Infrastructure

While training your people is half the battle, the other half is won or lost in your server room and on your network. Building a truly resilient infrastructure means making it an intentionally difficult and frustrating place for an attacker to operate. The goal is to make every step they take—from initial access to the final encryption—a major hurdle.
This starts with a fundamental shift in thinking. You have to move from a reactive "what if" mindset to a proactive, defense-in-depth strategy where your systems are designed to resist and contain threats from the get-go.
Implement the Principle of Least Privilege
One of the most effective security concepts you can put into practice is the principle of least privilege (PoLP). The idea is refreshingly simple: every single user, application, and system should only have the bare minimum permissions required to do its job. Nothing more.
Think about it. If an attacker compromises a user's account and that account has full administrative rights, it's game over. They own your network. But if that same compromised account can only access a few marketing folders, the attacker is stuck. The potential damage is immediately contained.
PoLP is your secret weapon against lateral movement. When an attacker can't jump from a compromised account to critical systems, a potential catastrophe is reduced to a minor, containable incident.
Getting this right isn't a one-time project; it's an ongoing discipline:
- Audit All User Accounts: Regularly comb through your access lists. Does the intern in marketing really need access to the finance server? Get rid of any permissions that aren't absolutely necessary.
- Lock Down Admin Rights: Standard user accounts should never have administrative privileges for day-to-day work. Reserve those powerful rights for dedicated IT staff performing specific tasks.
- Secure Network Shares: Make sure your shared drives and folders have granular permissions. Not everyone needs read/write access to every single file.
Isolate Critical Systems with Network Segmentation
Imagine your entire network is one big, open-plan office. If a fire starts in one corner, it can spread everywhere in minutes. Network segmentation is the equivalent of building sturdy firewalls between departments. It divides your network into smaller, isolated zones.
If ransomware hits one segment—say, the guest Wi-Fi or a temporary development environment—those digital walls prevent it from spreading to the crown jewels, like your production servers or financial databases.
This strategy is absolutely crucial in sectors like manufacturing. In a single quarter, Q2 2025, there were 657 industrial ransomware incidents globally, with manufacturing bearing the brunt of it at 65% of all cases. As detailed in the Dragos industrial ransomware analysis, these organizations survive by using strict network segmentation to isolate their factory floor systems from corporate networks. It’s a powerful lesson for any SMB.
To make this clearer, here’s a breakdown of some of the most essential technical controls and how they directly counter specific ransomware tactics.
Key Ransomware Prevention Controls for SMBs
| Control | Primary Goal | Ransomware Tactic Countered |
|---|---|---|
| Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) | Minimize damage by limiting access rights. | Lateral movement and privilege escalation. |
| Network Segmentation | Contain breaches within a small network zone. | Worm-like spreading and wide-scale encryption. |
| Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) | Detect and stop malicious behavior, not just files. | Zero-day exploits and fileless malware attacks. |
| Email Filtering & Security | Block malicious attachments and links at the source. | Phishing emails, the #1 ransomware delivery method. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Prevent unauthorized access even with stolen credentials. | Credential stuffing and brute-force password attacks. |
Implementing these controls creates multiple layers of defense, forcing an attacker to overcome several obstacles rather than just one.
Move Beyond Antivirus to Endpoint Detection and Response
Traditional antivirus software is like a security guard working from a list of known troublemakers. It’s good at stopping threats we’ve seen before, but it's easily bypassed by something new. Since modern ransomware operators are constantly changing their code, they can often walk right past old-school antivirus.
This is where Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions completely change the game.
Instead of just looking for known malicious files, EDR tools monitor for suspicious behavior on your endpoints—the laptops, desktops, and servers your business runs on. For instance, an EDR solution might notice a program like Microsoft Word suddenly trying to rapidly encrypt thousands of files. Your antivirus might miss that, but the EDR sees it for what it is—classic ransomware behavior—and shuts it down on the spot.
Managing these advanced tools effectively can be a full-time job. That's why many small businesses find that working with experts for managed IT and cybersecurity services is the best way to ensure their defenses are configured properly for maximum protection.
Creating a Ransomware-Proof Backup and Recovery Plan

Even with the best security tools and the sharpest team, you have to work from a simple, sobering assumption: a breach isn't a matter of if, but when. Real resilience isn’t just about putting up walls to stop attacks. It's about knowing you can get back on your feet quickly, with minimal damage, and without ever having to think about paying a ransom.
Your backup and recovery plan is the ultimate safety net that makes this possible. A good plan is more than just having copies of your files; it's a well-documented, frequently tested strategy that ensures you can restore everything when the worst happens. Without it, you’re left with only one terrible option: negotiating with criminals.
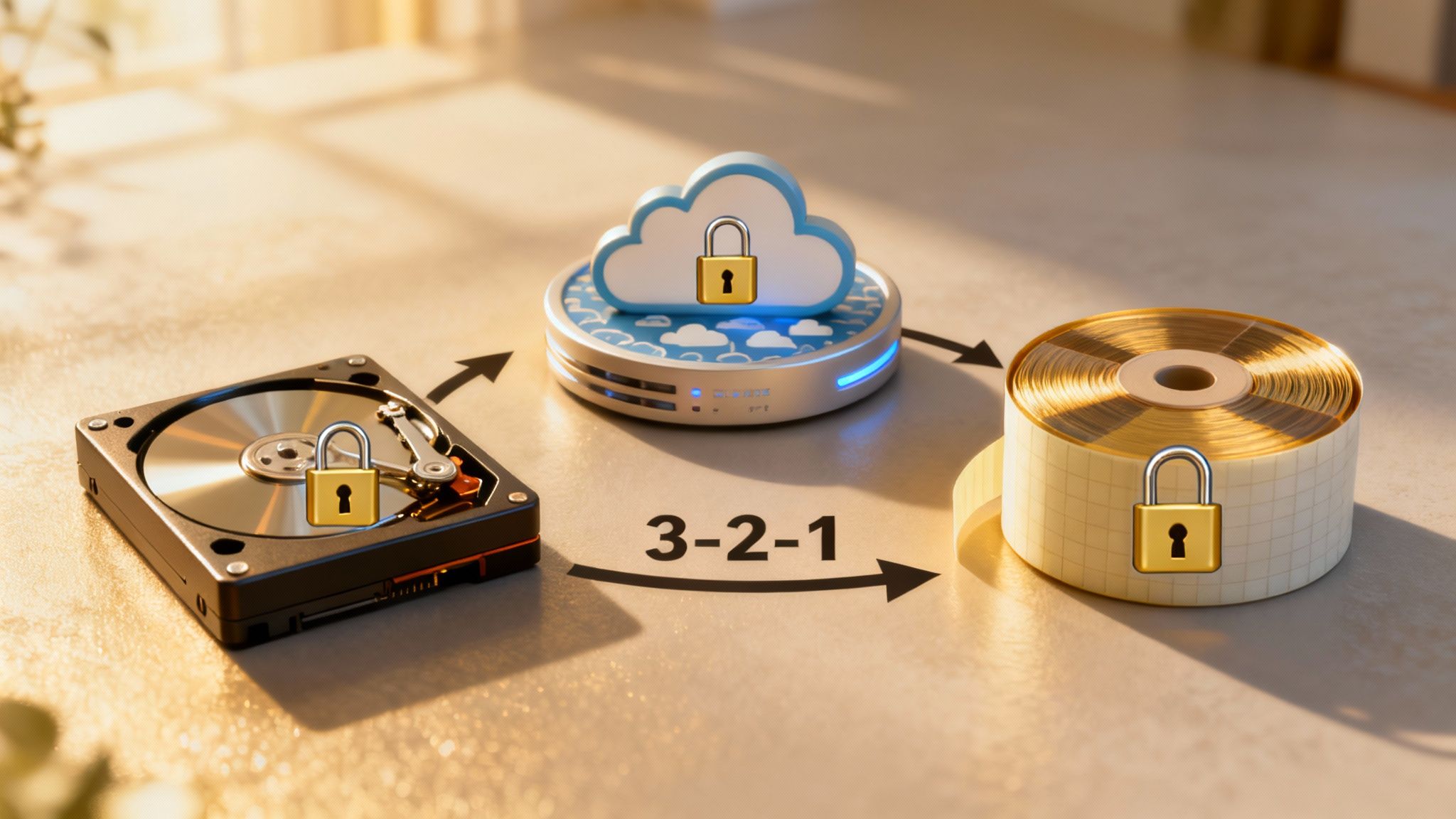
Master the 3-2-1-1-0 Backup Rule
The old 3-2-1 rule was a great starting point for years, but today's threats demand a few critical upgrades. The expanded 3-2-1-1-0 rule gives you a much stronger framework for making your data ransomware-proof.
Here’s the breakdown:
- 3 Copies of Your Data: Keep at least three separate copies of anything you can't afford to lose. This means your live production data plus at least two backups.
- 2 Different Media Types: Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Store backups on at least two different kinds of storage, like a local network-attached storage (NAS) device and a separate cloud storage service.
- 1 Copy Off-Site: One of those backup copies has to live somewhere physically separate from your office. If a fire, flood, or theft hits your primary location, that off-site backup is your lifeline.
- 1 Copy Offline or Immutable: This is the game-changer for fighting ransomware. One backup copy must be either "air-gapped" (physically disconnected from any network) or immutable (digitally locked so it can't be altered or deleted).
- 0 Errors: Your backups have to be tested and verified regularly. You need to be certain they're complete and error-free, so you know a recovery will actually work.
That last point about zero errors gets overlooked all the time, but it’s arguably the most critical. An untested backup is just a hope, not a plan.
Embrace Immutable and Air-Gapped Backups
The concept of an immutable backup is your secret weapon against sophisticated ransomware that actively hunts down and encrypts your backup files. Attackers know that if they can destroy your ability to recover, you're far more likely to pay up.
Immutable storage makes your backup data read-only for a specific period. Once the data is written, it cannot be changed or deleted by anyone—not even an administrator with the highest-level credentials. If ransomware gets into your network and tries to encrypt these protected backups, it simply hits a digital brick wall.
Air-gapped backups provide a similar level of protection, just through physical separation instead of digital locks.
Think of an air-gapped backup like keeping a copy of your most important documents in a bank's safe deposit box. A criminal on your office network has no physical way to get to that box.
For a small business, this could be as straightforward as backing up data to an external hard drive that you then unplug and store securely somewhere else. On the cloud side, providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Backblaze now offer "object lock" features that create this immutability digitally, which is a fantastic and scalable modern solution.
Define Your Recovery Objectives Before a Crisis
When an attack hits, the pressure is immense. You can’t afford to be making critical decisions on the fly. That's why you need to figure out your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) long before you ever need them.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): This is the stopwatch on your recovery. It’s the absolute maximum amount of time your business can afford to be down after an incident. Is it four hours? A full business day? Your RTO dictates how fast your recovery process needs to be.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): This measures how much data you can stand to lose. If your RPO is one hour, it means you need backups running at least every hour, so you never lose more than 60 minutes of work.
Knowing these two numbers turns your recovery plan from a vague idea into a precise, actionable strategy. It sets clear expectations for everyone, from the IT team to the CEO, and ensures the recovery process meets the actual needs of the business. This is also why you test your restores—it not only verifies your backups but rehearses your entire plan, helping turn a potential crisis into a manageable procedure.
Bolstering Your Defenses with Modern Tools and Cyber Insurance
Once you’ve locked down the fundamentals like backups and employee training, it’s time to layer in more advanced protection. You simply can't watch every file and network connection manually—it's an impossible task for any team. This is where modern security tools, especially those driven by AI, become your most valuable players.
At the same time, you need a financial backstop. Think of cyber insurance as a critical part of your risk management plan, but remember, it’s not a replacement for strong security practices.
Let AI and Machine Learning Do the Heavy Lifting
Traditional antivirus software is great at catching known malware, but it's always playing catch-up. Attackers constantly tweak their ransomware's digital signature to sneak past these older defenses. This is precisely why the security world has shifted its focus from what a file is to what it does.
The new standard here is Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR). Instead of just scanning files against a blacklist of known viruses, EDR tools actively monitor for suspicious behavior. For instance, if a legitimate tool like PowerShell suddenly starts encrypting hundreds of files on your server, an EDR solution recognizes this as a classic ransomware tactic and can shut it down instantly.
This proactive stance is a huge win for SMBs. The data shows that using artificial intelligence and automation in cybersecurity results in an average annual cost saving of $2.22 million per organization by stopping breaches before they escalate. You can get a closer look at these trends by checking out the latest insights on global cyber attack patterns at industrialcyber.co.
The infographic below paints a clear picture of how this modern defense workflow combines technology with strategic risk management.
As you can see, it's a cycle: you deploy advanced tools to protect your assets, and you secure a financial backstop to manage the remaining risk, creating a much more resilient operation.
Demystifying Cyber Insurance
There's a lot of confusion about what cyber insurance actually is. It's not a "get out of jail free" card that lets you off the hook for poor security. In fact, it’s the complete opposite. Today, insurers are demanding that businesses prove they have specific, robust security controls in place before they'll even consider offering a policy.
Think of it as a partnership. The insurance provider needs you to be a low-risk client, and you want to prevent an attack in the first place. Your goals are perfectly aligned.
Getting a cyber insurance policy is no longer just about filling out a form. It's a rigorous audit of your security posture. If you can't prove you're a low-risk client, you won't get coverage.
When you apply, get ready for an in-depth review. You’ll need to provide hard evidence that you meet their standards, which almost always include:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Is MFA enabled on all email accounts, remote access points, and administrator logins? This is a deal-breaker for most insurers.
- Backups and Recovery: Can you prove you have offline, immutable backups? More importantly, can you show you've actually tested them?
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Many carriers now flat-out require an EDR solution to be deployed across all your computers and servers.
- Employee Training: You'll need to show proof of a consistent, ongoing security awareness and phishing simulation program for your team.
Meeting these strict requirements can feel overwhelming. Working with a provider of managed IT and cybersecurity services can streamline the process, ensuring you have the right controls in place to not only get insured but also to genuinely protect your business from an attack.
Crafting a Real-World Incident Response Plan
Let's be realistic: even with the best defenses in the world, you have to operate as if a breach is inevitable. It’s not a matter of if, but when.
When that day comes, the minutes and hours that follow are absolutely critical. Panic sets in, people make mistakes, and without a clear plan, a containable problem can quickly spiral into a full-blown catastrophe that shuts your business down for good. This is where your Incident Response (IR) plan comes in—it’s your playbook for chaos.
Think of it less as a dusty binder on a shelf and more as a field guide for your team to use under immense pressure. It replaces frantic guesswork with a calm, step-by-step process. Everyone knows their job, who to call, and what to do next. The goal is to shift from reactive fear to a controlled, measured response that limits the damage and gets you back on your feet.
Remember, the average business hit with ransomware faces 20 days of downtime. A solid, well-rehearsed plan can slash that number dramatically.
The Six Phases of Incident Response
A good IR plan isn’t just a random to-do list; it follows a proven structure that breaks the response into manageable stages. Understanding these phases helps you build a playbook that covers everything from the initial alert to the final post-mortem.
Here’s a quick rundown of the essential stages:
- Preparation: This is all the work you do before the phone rings at 3 AM. It’s about building the plan, getting your team together, and making sure all your tools and contacts are ready to go.
- Identification: The moment an alarm bell goes off, this phase kicks in. The mission is to figure out if it's a real threat, what you're dealing with, and how bad it might be.
- Containment: Once you've confirmed an attack, the immediate priority is to stop the bleeding. This means isolating infected machines and servers to prevent the ransomware from spreading like wildfire across your network.
- Eradication: With the threat boxed in, you move to eliminate it completely. This isn't just about deleting the malware; it's about finding and patching the security hole the attackers used to get in.
- Recovery: Now that the threat is gone, you can start rebuilding. This phase is all about restoring your systems from clean, trusted backups and carefully bringing your operations back online.
- Lessons Learned: After the dust settles, this is arguably the most important step. You have to conduct a brutally honest review of what happened, what went right, what went wrong, and how you can harden your defenses to stop it from happening again.
Assembling Your Core Response Team
A plan is worthless without the right people to execute it. One of the most critical parts of the preparation phase is deciding exactly who is on your response team. You absolutely cannot be figuring this out in the middle of a crisis.
Your team needs to be more than just your tech people. While your IT or security lead will be quarterbacking the technical side, a ransomware attack is a business problem that requires input from across the company.
The single biggest mistake I see is an IR plan built entirely by the IT department. A ransomware attack isn't a server issue; it's a business crisis. You need legal, communications, and executive leadership at the table from the very beginning.
Make sure your response team includes stakeholders from these key areas:
- Executive Leadership: Someone with the authority to make major decisions, approve emergency spending, and lead the overall crisis management strategy.
- IT and Security: The technical experts who will investigate the breach, contain the threat, and lead the recovery effort.
- Legal Counsel: To navigate the tricky waters of data breach notification laws, regulatory compliance, and potential liabilities.
- Human Resources: To manage all internal communications, field employee questions, and keep morale from cratering.
- Public Relations/Communications: To control the narrative and handle all external messaging to your customers, partners, and—if necessary—the media.
For every role, write down their name, contact info (including a personal cell number), and their specific duties during an incident. You should also pre-identify your key external partners, like a cybersecurity forensics firm or your cyber insurance provider. Put all their contact details on a single "first call" sheet. Trust me, that one page will be the most valuable part of your entire plan when things go wrong.
Answering Your Top Ransomware Prevention Questions
When you're trying to defend your business from something as nasty as ransomware, it's natural to have questions. As an SMB owner or IT manager, you need straight, practical answers to figure out where to focus your efforts and make smart decisions that will actually protect you.
Let's dive into some of the most common questions we hear from businesses trying to navigate this threat.
What Is the Single Most Important First Step?
If you only do one thing today to stop ransomware in its tracks, make it this: turn on Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) everywhere you possibly can. I'm talking email, remote access tools like your VPN, and especially all administrator accounts.
Why is this so crucial? Because attackers love to use stolen passwords to just walk right in. It's the easiest way for them.
MFA essentially slams that door shut. By asking for a second piece of proof—usually a code from a phone app—it creates a barrier that a stolen password alone can't break. While lots of other security measures are important, enabling MFA gives you the biggest security boost, right away.
Are Cloud Services Like Microsoft 365 Safe?
This is a huge and frankly dangerous misconception. Yes, cloud giants like Microsoft and Google have phenomenal security protecting their own infrastructure. But the data you put into their services? That's your responsibility to protect.
Think about it: if your computer gets infected with ransomware, it can easily encrypt all the files in the OneDrive or Google Drive folder it's synced with. Or, an attacker could phish your cloud login credentials, sign in as you, and just delete everything.
Don't make the mistake of assuming your cloud provider is also your data backup. Treat your cloud data with the same care as your in-house servers. Lock it down with MFA, be strict about who has access, and most importantly, back it up independently.
Should My Business Ever Consider Paying the Ransom?
Every law enforcement agency, from the local level to the FBI, is crystal clear on this: do not pay the ransom. It's tempting when you're in a panic, but paying is a losing game for several reasons.
- You're dealing with criminals. There's absolutely no guarantee you'll get a working decryption key. We've seen cases where businesses pay and get nothing in return.
- You're funding their next attack. Every dollar paid proves their business model works, fueling their operations and encouraging them to hit more businesses. You might even end up on a "willing to pay" list, making you a target for future attacks.
- The threat isn't really gone. Even if you get a key, the malware they used to get in is often left behind. The backdoors are still there, leaving you wide open for a repeat performance.
The only reliable way out of a ransomware mess is having a solid, tested backup and recovery plan. When you can confidently restore your data, the ransom demand becomes a non-issue. For a deeper look at building a full prevention strategy, this comprehensive guide on how to prevent ransomware attacks is an excellent resource. It shifts your focus from payment to recovery, which is exactly where it should be.
At Defend IT Services, we help San Antonio businesses build security plans that are tough enough to make these questions easy. From getting MFA rolled out to designing ransomware-proof backups, we bring the expertise to keep you running. Secure your business with our managed cybersecurity solutions.

