In today's business environment, your email inbox is not just a communication tool; it is the primary entry point for cyberattacks. From sophisticated phishing schemes designed to steal credentials to ransomware-laden attachments that can paralyze your operations, the threats are constant and evolving. For businesses in San Antonio, especially those in regulated industries like healthcare and finance, the stakes are incredibly high. A single email-based breach can lead to devastating financial loss, regulatory penalties, and irreparable damage to your reputation. Simply having an email account makes your organization a target.
However, deploying a robust defense is not just possible; it's essential for survival. This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a detailed, actionable playbook of nine essential email security best practices. We will dissect the technical protocols, human-centric strategies, and policy frameworks that create a multi-layered shield for your organization's most critical data. Whether you are a small business needing managed IT services, a multi-location company requiring 24/7 threat monitoring, or a growing team planning a cloud migration, these insights are designed for you.
Inside, you will find practical steps for implementing everything from advanced email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to comprehensive security awareness training. We will explore the non-negotiable role of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), the necessity of email encryption, and how Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies can safeguard your sensitive information. Implementing these practices will transform your email from your biggest vulnerability into a well-defended fortress, ensuring compliance, protecting client data, and securing your business's future.
1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Email Accounts
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is one of the most effective email security best practices you can implement. It moves beyond a single password, which can be stolen or guessed, by requiring a second (or third) verification factor to grant access. This layered defense works on the principle of combining something you know (your password) with something you have (a phone or security key) or something you are (a fingerprint or face scan).
Even if a cybercriminal successfully acquires your password through a phishing attack or data breach, MFA acts as a critical barrier, preventing them from accessing your email account and the sensitive data within. The effectiveness of this approach is well-documented; Microsoft famously reported a 99.9% reduction in account compromise for users who enabled MFA.

Actionable Tips for Implementing MFA
Simply turning on MFA is a great start, but optimizing its deployment ensures maximum security for your organization.
- Prioritize Authenticator Apps Over SMS: While SMS-based codes are better than nothing, they are vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks. Encourage users to adopt more secure authenticator apps like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy.
- Deploy Hardware Keys for High-Risk Users: For executives, finance personnel, or system administrators, implement FIDO2-compliant hardware security keys (like a YubiKey). These physical devices provide the strongest protection against phishing and are virtually impossible to duplicate remotely. Cloudflare famously implemented these for all employees, resulting in zero successful phishing attempts.
- Consider Adaptive MFA: Modern systems can use adaptive or risk-based authentication. This technology evaluates login attempts based on context like location, device, or time of day. It can enforce stricter MFA requirements for high-risk scenarios while providing a smoother user experience for routine logins.
- Educate and Train Your Team: Ensure your staff understands why MFA is crucial and how to use it correctly. Provide clear instructions for setting it up and managing backup codes. Store these backup codes securely in a password manager or an offline, protected location, never in plain text on a computer.
2. Email Encryption (End-to-End and Transport Layer)
Email encryption is a foundational email security best practice that protects the confidentiality of your communications. It works by converting the readable plaintext of an email into unreadable ciphertext, ensuring that only authorized parties with the correct key can decipher the message. This protection is critical for preventing unauthorized access, whether your email is in transit between servers or at rest on a server.
Two primary forms of encryption safeguard your messages. Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts the connection between email servers, like a secure tunnel protecting a delivery truck on the highway. End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) goes further, encrypting the message content itself, which can only be unlocked by the sender and the intended recipient. Even the email provider cannot access E2EE content, a model famously used by services like ProtonMail to provide zero-access privacy. For regulated industries like healthcare and finance, encryption is not just a best practice; it is often a compliance mandate.
This concept map illustrates the core components of a comprehensive email encryption strategy, showing how different methods work together to protect data.
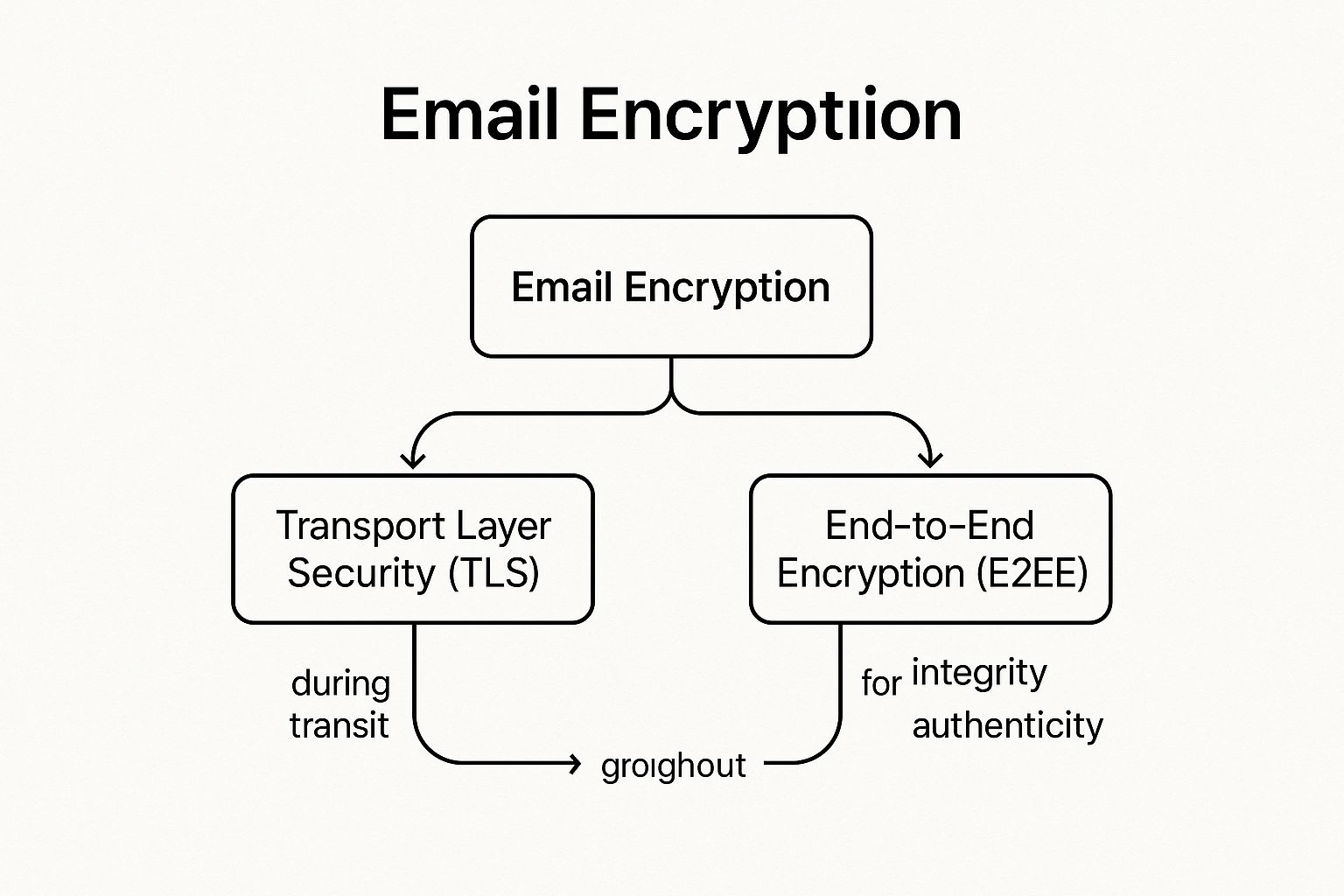
The visualization clarifies that a robust approach combines both transit (TLS) and content-level (E2EE) protection, complemented by digital signatures to verify sender identity and message integrity.
Actionable Tips for Implementing Email Encryption
Implementing encryption requires a strategic approach that blends technology, policy, and user awareness to protect sensitive information effectively.
- Enforce Strong Transport Layer Security: Mandate modern encryption protocols for all email transmissions. Configure your email servers to require TLS 1.2 or higher and implement mechanisms like STARTTLS for opportunistic encryption. For maximum security, use MTA-STS (Mail Transfer Agent Strict Transport Security) to ensure external servers only connect to yours using an encrypted channel.
- Deploy S/MIME or PGP for Sensitive Communications: For enterprise environments, especially in legal or healthcare sectors, implement Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) or Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) for true end-to-end encryption. S/MIME integrates well with corporate public key infrastructures (PKI), while PGP is a long-standing standard for individual and organizational data protection.
- Automate Encryption with Gateways and DLP: Use a secure email gateway or Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solution to automate encryption based on predefined policies. These tools can scan outbound emails for sensitive data patterns, such as credit card numbers or patient information, and automatically apply encryption before the message leaves your network, reducing reliance on user discretion.
- Establish Clear Policies and Provide Training: Define exactly what types of information must always be encrypted, such as financial data, intellectual property, or personally identifiable information (PII). Train employees on how to use encryption tools and when they are required to do so. Ensure encryption keys are securely backed up and managed with strict access controls.
3. SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Email Authentication Protocols
Implementing email authentication protocols is a fundamental email security best practice for validating a sender's identity. This trio of standards, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, works in concert to prevent unauthorized use of your domain, effectively shutting down spoofing and phishing attempts. They act as a digital passport for your emails, proving to receiving servers that the message is legitimately from you and has not been altered in transit.
These protocols are the bedrock of modern email trust. SPF (Sender Policy Framework) specifies which mail servers are permitted to send email on behalf of your domain. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) adds a cryptographic signature to messages, ensuring their integrity. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance) then ties them together, instructing receiving servers on how to handle unauthenticated mail and providing crucial reports on your email ecosystem. For a foundational understanding of how to protect your domain from impersonation, consider understanding email authentication protocols.
Actionable Tips for Implementing Authentication Protocols
Proper configuration is key to leveraging the full power of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. A phased approach prevents disrupting legitimate email flow.
- Start with a Monitoring Policy: Begin your DMARC implementation with a
p=nonepolicy. This allows you to collect data on all mail sent using your domain, both legitimate and fraudulent, without affecting email delivery. - Analyze DMARC Reports: Use the aggregate reports generated by your DMARC policy to identify all legitimate sending sources, including third-party services like marketing platforms or CRMs. Ensure they are correctly configured for SPF and DKIM.
- Gradually Increase Enforcement: Once you are confident that all legitimate mail is authenticating correctly, move your DMARC policy to
p=quarantine(sends unauthenticated mail to spam) and finally top=reject(blocks it entirely). This gradual enforcement minimizes risk. - Maintain Your SPF Record: An SPF record is limited to 10 DNS lookups. Regularly audit and clean up your record to remove obsolete services and stay within this limit to ensure it functions correctly. For all subdomains, use the 'sp' tag in your primary DMARC record to apply your policy consistently.
4. Security Awareness Training and Phishing Simulation
Technical controls are crucial, but the human element remains a primary target for cybercriminals. Security Awareness Training and Phishing Simulation is one of the most vital email security best practices because it transforms your employees from a potential vulnerability into a powerful line of defense. This approach educates users on how to identify and respond to social engineering tactics, malicious links, and suspicious attachments, directly strengthening your organization's security posture from within.
Regular training, paired with realistic but harmless phishing simulations, creates a security-conscious culture. The data proves its effectiveness; Verizon's 2023 DBIR found that organizations with consistent training suffer 50% fewer security incidents. Similarly, Microsoft reports that well-run simulation programs can reduce employee susceptibility to phishing by over 50% within the first year.

Actionable Tips for Implementing Training and Simulation
A successful program is more than just an annual slideshow. It requires a strategic, continuous approach to truly change user behavior and enhance overall email security.
- Benchmark and Personalize: Start with a baseline phishing simulation to assess your team's current vulnerability. Use these results to tailor training content to address specific departmental risks, such as wire transfer fraud for the finance team or credential theft for IT administrators.
- Maintain a Consistent Cadence: Conduct formal training quarterly, at a minimum. Supplement this with monthly phishing simulations that use varied scenarios reflecting current events and real-world threats (like tax season scams or holiday-themed attacks) to keep skills sharp.
- Focus on Education, Not Punishment: The goal is improvement, not blame. When an employee clicks a simulated phishing link, provide immediate, bite-sized training that explains the red flags they missed. Conversely, implement a positive reinforcement system to reward employees who correctly report suspicious emails.
- Make Reporting Easy: Deploy a simple, one-click "Report Phishing" button in your email client. Removing friction from the reporting process significantly increases the chances that employees will alert your IT or security team to a potential threat, allowing for a faster response. As you build this security-first culture, you can learn more about the importance of cybersecurity for growing businesses and how it underpins sustainable success.
5. Advanced Threat Protection and Email Filtering
Advanced Threat Protection (ATP) solutions provide a crucial layer of defense that goes far beyond standard spam filters. These systems use sophisticated technologies like machine learning, sandboxing, and URL rewriting to identify and neutralize threats that are designed to bypass basic security. Implementing ATP is one of the most proactive email security best practices for defending against zero-day malware, sophisticated phishing, and business email compromise (BEC).
Unlike traditional filters that rely on known signatures, ATP analyzes the behavior of incoming emails in real time. It can detonate suspicious attachments in a safe, isolated "sandbox" environment to see if they are malicious or rewrite links to scan them for threats when a user clicks them. This dynamic analysis is key to stopping novel and evolving attack methods before they reach an employee's inbox. For example, Microsoft Defender for Office 365 and Proofpoint have successfully blocked billions of advanced threats for their customers, preventing massive financial and data losses.
Actionable Tips for Implementing ATP
Deploying an ATP solution is a significant step, but proper configuration is essential for it to be truly effective. Partnering with a provider of managed IT and cybersecurity services can help ensure these systems are optimized for your specific business needs.
- Enable All Key Protection Features: Do not just turn on the basic filtering. Ensure that sandboxing for attachments, URL defense (link rewriting), and impersonation protection are all fully enabled and configured to protect high-value targets like executives and finance staff.
- Layer ATP with Native Security: Use ATP as an enhancement, not a replacement, for the built-in security features of your email platform (like Exchange Online Protection). This creates a defense-in-depth strategy where multiple layers work together.
- Configure Policies Based on Risk: Apply more stringent scanning policies to high-risk user groups. For instance, the finance department might have stricter rules for attachments and wire transfer-related keywords than the marketing team.
- Regularly Review Quarantined Items: Periodically check the quarantine log to identify legitimate emails that were incorrectly flagged (false positives) and release them. This helps fine-tune the system's accuracy and ensures important communications are not missed.
- Integrate with Your Broader Security Ecosystem: Connect your ATP solution with your Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system. This provides a holistic view of threats, allowing your security team to correlate email-based attacks with other events across your network for a faster, more effective response.
6. Strong Password Policies and Password Manager Usage
Even the most advanced email security best practices can be undermined by a weak password. Establishing a strong password policy is a foundational defense that dictates requirements for complexity, length, and history, making it significantly harder for attackers to brute-force or guess their way into an account. However, policies alone are often impractical for users, which is where password managers become an essential complementary tool.
Password managers generate, securely store, and automatically fill complex, unique passwords for every account. This combination removes the human element of password fatigue and the dangerous habit of reusing credentials. By pairing a robust policy with a user-friendly tool, organizations can dramatically reduce the risk of credential-based attacks, which remain a primary vector for email compromise.

Actionable Tips for Passwords and Managers
A modern approach to password security focuses on practicality and strength, moving away from outdated, ineffective rules.
- Prioritize Length and Passphrases: Following NIST guidelines, enforce a minimum password length of 12-16 characters. Encourage the use of passphrases (e.g., "Correct-Horse-Battery-Staple"), which are long, memorable for users, and extremely difficult for computers to crack.
- Deploy an Enterprise Password Manager: Implement a trusted enterprise password manager like Bitwarden or 1Password. These tools offer centralized administration, secure sharing, and auditing capabilities, allowing you to enforce policies and monitor password health across the organization. For example, some enterprises have eliminated over 80% of password-reset help desk tickets after deployment.
- Eliminate Mandatory Periodic Resets: Contrary to old advice, NIST now recommends against forced, periodic password changes unless a compromise is suspected. This practice often leads to users creating weak, predictable password variations. Instead, focus on detecting actual breaches using services like HaveIBeenPwned.
- Secure the "Keys to the Kingdom": The password manager is critical infrastructure. Mandate a strong, unique master password for the manager itself and, most importantly, protect every user's vault with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). The 2022 LastPass breach highlighted that even with a vault compromise, strong master passwords and encrypted data kept user credentials safe.
7. Email Attachment and Link Scanning Policies
Email Attachment and Link Scanning Policies form a critical, automated line of defense against malware and phishing attacks. Instead of relying solely on end-users to spot malicious content, this best practice involves using technology to systematically inspect all incoming (and outgoing) emails. These systems scan attachments for viruses and malware, analyze embedded links for malicious destinations, and can even block high-risk file types before they ever reach an inbox.
This proactive approach acts as a digital gatekeeper, effectively neutralizing threats before a user has the chance to interact with them. For example, during the WannaCry ransomware outbreak, organizations with robust attachment scanning policies automatically blocked the infected emails, preventing widespread devastation. Similarly, advanced link scanning can thwart sophisticated phishing attacks where a link initially appears benign but is later redirected to a credential-harvesting site. This automation is a cornerstone of modern email security best practices.
Actionable Tips for Implementing Scanning Policies
A well-configured scanning policy is more than just a simple antivirus check; it's a multi-layered strategy to identify and neutralize a wide range of threats.
- Block High-Risk Executables: Immediately configure your email gateway to block dangerous file types by default. This includes
.exe,.bat,.vbs,.js,.ps1, and.scrfiles, which are commonly used to deliver malware. - Enable Macro and Script Blocking: Many attacks, like the Emotet malware campaigns, hide malicious code within macros in Microsoft Office documents. Configure your system to scan and block or quarantine all Office files containing macros from external sources.
- Implement Time-of-Click URL Protection: Cybercriminals often "weaponize" links after an email is delivered. Use a service that rewrites URLs in incoming emails. When a user clicks the link, it is first routed through a security service that performs a real-time scan, blocking access if the destination has become malicious.
- Scan Inside Archives: Malware is frequently hidden within compressed files like
.zipand.rarto bypass basic scanners. Ensure your security solution is configured to decompress and inspect the contents of these archives. - Consider Content Disarm and Reconstruction (CDR): For organizations with a low tolerance for risk, CDR technology rebuilds files from scratch, stripping out any potentially malicious active content while preserving the file's usability. This is highly effective against zero-day exploits hidden in common file types like PDFs and images.
8. Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
Maintaining up-to-date software is a foundational email security best practice that is often overlooked. Cybercriminals actively scan for and exploit known vulnerabilities in email clients, servers, operating systems, and related applications. Failing to apply security patches promptly leaves a wide-open door for attackers to compromise systems, steal credentials, deploy ransomware, or exfiltrate sensitive data. A disciplined patch management process is your first line of defense against these well-documented threats.
The consequences of delayed patching are severe. In 2021, the Microsoft Exchange Server "ProxyLogon" vulnerability was exploited on a massive scale, affecting tens of thousands of organizations that had not applied the available patch. Similarly, the infamous WannaCry ransomware spread rapidly by exploiting an unpatched Windows vulnerability, crippling businesses globally despite a patch being available for months. These incidents underscore that having a patch is not enough; applying it quickly is what matters.
Actionable Tips for Patch Management
A reactive approach to patching is insufficient. A proactive, policy-driven strategy is essential for minimizing your organization's window of vulnerability.
- Establish a Formal Patch Management Policy: Define Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for different severity levels, such as requiring critical patches to be applied within 48 hours and high-priority patches within one week. This removes ambiguity and ensures timely action.
- Automate Where Possible: Enable automatic updates for endpoint software like email clients (Outlook, Thunderbird), web browsers, and antivirus solutions. For servers and infrastructure, use centralized patch management tools like Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager or ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus to automate deployment.
- Prioritize Based on Risk: Not all patches are equal. Use the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) score, combined with threat intelligence on active exploitation and asset criticality, to prioritize which updates to deploy first. A vulnerability on a public-facing email server is a higher priority than one on an isolated internal machine.
- Test Before Deploying: Whenever possible, test patches in a non-production or staging environment before rolling them out across the entire organization. This helps identify potential compatibility issues or operational disruptions and allows for the creation of a rollback plan in case a patch causes problems.
9. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Email Monitoring
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a crucial email security best practice that acts as a digital gatekeeper for your sensitive information. It involves a set of tools and processes designed to monitor, detect, and block confidential data from being sent outside your organization via email, whether accidentally or maliciously. DLP systems work by inspecting email content and attachments for predefined sensitive information patterns, such as credit card numbers, health records, or proprietary source code.
This technology is essential for preventing costly data breaches, ensuring regulatory compliance (like HIPAA or GDPR), and protecting intellectual property. For example, a healthcare organization can automatically block an email containing unencrypted patient data, or a tech firm can prevent a departing employee from emailing confidential CAD files to a personal account. By enforcing data handling policies at the email gateway, DLP provides a powerful defense against both insider threats and unintentional human error.
Actionable Tips for Implementing DLP
A successful DLP strategy requires careful planning and continuous refinement. Simply turning on a blocking policy can disrupt business, so a phased approach is recommended.
- Start in Monitoring Mode: Before enforcing any blocking rules, run your DLP solution in a monitoring-only mode. This will help you understand how sensitive data flows through your email system without interrupting workflows and allows you to identify legitimate business cases for data sharing.
- Prioritize High-Risk Data: Begin by creating policies that focus on your most critical and easily identifiable data types. This includes Personally Identifiable Information (PII), financial data (like credit card numbers), and protected health information (PHI). This targeted approach provides immediate value while you develop more complex rules.
- Use Data Classification: Implement a data classification policy where users label documents (e.g., Public, Internal, Confidential). This complements automated DLP detection by allowing your system to enforce rules based on how your team has explicitly classified the information's sensitivity.
- Develop Tiered Policies and User Education: Create policies that take different actions based on risk. For instance, a low-risk violation might trigger a user notification explaining the policy, while a high-risk attempt to send a customer database could be blocked outright and trigger an alert to security personnel. For more advanced implementation strategies, local cybersecurity and IT solutions can provide guidance.
- Integrate with Encryption: Configure your DLP system to automatically encrypt emails containing sensitive information rather than just blocking them. This allows legitimate business communications to proceed securely while still protecting the data in transit.
Email Security Best Practices Comparison Matrix
| Security Measure | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Email Accounts | Moderate – requires device/setup management | Requires secondary devices or apps | Drastically reduces unauthorized access (~99.9%) | Protecting user accounts, high-risk access control | Strong security layer, compliance support |
| Email Encryption (End-to-End and Transport Layer) | High – complex key and certificate management | High – digital certificates & key management | Protects data confidentiality and integrity | Sensitive data communication, regulatory compliance | Confidentiality, message integrity, non-repudiation |
| SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Email Authentication Protocols | High – DNS and policy configuration, ongoing maintenance | Moderate – IT coordination needed | Reduces spoofing and phishing, improves deliverability | Domain reputation protection, phishing prevention | Brand protection, email trust & deliverability |
| Security Awareness Training and Phishing Simulation | Low to Moderate – ongoing campaigns and monitoring | Moderate – training resources and platforms | Decreases successful phishing attacks & increases reporting | Employee education, phishing readiness | Human firewall, measurable behavior improvement |
| Advanced Threat Protection and Email Filtering | High – integration of AI/ML and sandboxing tech | High – licensing and expert tuning | Detects and blocks sophisticated email threats | Advanced malware, zero-day attack prevention | Comprehensive threat detection, automated response |
| Strong Password Policies and Password Manager Usage | Low – policy enforcement and tool deployment | Low to Moderate – password manager deployment | Reduces credential attacks, improves user password hygiene | General account security, password management | Practical password security, breach alerts |
| Email Attachment and Link Scanning Policies | Moderate to High – scanning engines and policy setup | Moderate – antivirus and URL scanning systems | Prevents malware and phishing via attachments/links | Malware/ransomware prevention, safe attachment control | Multi-layered malware defense, reduces attack surface |
| Regular Software Updates and Patch Management | Moderate – patch testing & deployment processes | Moderate – patch management tools | Closes vulnerabilities, ensures system stability | Maintaining secure email infrastructure | Reduces exploit risks, compliance, system reliability |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Email Monitoring | High – policy creation, tuning, and monitoring | High – content inspection and analytics | Prevents data leaks and ensures compliance | Protecting sensitive data, regulatory environments | Data protection, compliance, insider threat mitigation |
From Vulnerability to Vigilance: Activating Your Email Defense Strategy
Securing your organization's most critical communication channel is not a single project with a finish line; it is an ongoing commitment to vigilance and adaptation. Throughout this guide, we've navigated the essential layers of a robust email security framework. From the foundational technical protocols of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC that validate sender identity, to the non-negotiable user-level protection of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), each practice serves as a critical link in your defensive chain.
We've established that technology alone is an incomplete solution. Advanced threat protection and sophisticated email filtering are powerful tools, but they must be paired with an equally strong human firewall. This is where security awareness training and realistic phishing simulations transform your employees from potential targets into proactive defenders. The ultimate goal is to cultivate a security-first culture where every team member understands their role in protecting sensitive information. This proactive mindset is the cornerstone of effective email security best practices.
Synthesizing Your Defense: Key Takeaways
The true strength of your email security posture lies not in implementing one or two of these measures, but in weaving them together into a comprehensive, multi-layered strategy. Think of it as a holistic system where each component supports the others.
- Technology and Policy Hand-in-Hand: Your strong password policies are only effective if they are enforced and complemented by MFA. Your Data Loss Prevention (DLP) rules gain their power from clear policies that define what sensitive data is and how it should be handled.
- Authentication is Non-Negotiable: The trio of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC is no longer optional for any serious business. They are the digital passports of email, preventing brand impersonation and protecting your customers and partners from spoofing attacks that could tarnish your reputation.
- The Human Element is Your Greatest Asset (or Liability): An employee who can spot a sophisticated phishing attempt is more valuable than the most expensive filtering software. Investing in continuous training directly reduces your risk of a breach caused by human error, which remains a leading cause of security incidents.
Activating Your Next Steps
Moving from knowledge to action is the most crucial step. For businesses in San Antonio, especially those in regulated industries like healthcare or finance, implementing these email security best practices can feel overwhelming. The key is to start with a structured approach.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis: Begin by assessing your current state. Are you using DMARC? Is MFA deployed for all users? Is your employee training program ad-hoc or formalized? Identifying your weakest links will prioritize your efforts.
- Prioritize Implementation: Start with the highest-impact items. Implementing MFA across all email accounts and configuring email authentication protocols often provide the biggest immediate security uplift.
- Automate and Monitor: Deploy tools that automate routine security tasks, such as email filtering and patch management. This frees up your IT resources to focus on strategic threat hunting and incident response. Continuous monitoring ensures you can detect and react to threats in real-time.
Mastering these concepts is invaluable. It transforms email from a significant vulnerability into a secure and reliable business tool. It protects your financial assets, safeguards sensitive client data, ensures regulatory compliance (like HIPAA), and ultimately, preserves the trust you have built with your customers. To further enhance your understanding and defense, explore broader insights on email security strategies and emerging threats. A proactive, educated approach is your best defense against the constantly evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Navigating the complexities of a multi-layered security strategy requires expertise and constant attention. Defend IT Services specializes in implementing and managing these advanced email security best practices for businesses, providing 24/7 monitoring and expert guidance. Let us handle your security, so you can focus on growing your business with confidence by visiting Defend IT Services.

